CAUTION:
Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
DESCRIPTION:
Each gram of Vetromax ointment contains gentamicin sulfate USP equivalent
to 3 mg gentamicin base; betamethasone valerate USP equivalent to 1 mg betamethasone; and
10 mg clotrimazole USP in a mineral oil-based system containing a plasticized hydrocarbon gel.
PHARMACOLOGY:
Gentamicin: Gentamicin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against a wide variety of pathogenic gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. In vitro tests have determined that gentamicin is bactericidal and acts by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susceptible microorganisms. Specifically, gentamicin is active against the following organisms commonly isolated from canine ears: Staphylococcus aureus, other Staphylococcus spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., and Escherichia coli.
Betamethasone: Betamethasone valerate is a synthetic adrenocorticoid for dermatologic use.
Betamethasone, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of corticosteroid activity and a
slight degree of mineralocorticosteroid activity. Betamethasone valerate, the 17-valerate ester of
betamethasone, has been shown to provide anti-inflammatory and antipruritic activity in the
topical management of corticosteroid-responsive otitis externa.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal, intact skin. Inflammation can increase
percutaneous absorption. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled
through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids.
Clotrimazole: Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that is used for the treatment
of dermal infections caused by various species of pathogenic dermatophytes and yeasts. The
primary action of clotrimazole is against dividing and growing organisms.
In vitro, clotrimazole exhibits fungistatic and fungicidal activity against isolates of Trichophyton
rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum canis, Candida
spp., and Malassezia pachydermatis (Pityrosporum canis). Resistance to clotrimazole is very
rare among the fungi that cause superficial mycoses.
In an induced otitis externa infected with Malassezia pachydermatis, 1% clotrimazole in the
Vetromax ointment vehicle was effective both microbiologically and clinically in terms of
reduction of exudate odor and swelling.
In studies of the mechanism of action, the minimum fungicidal concentration of clotrimazole
caused leakage of intra-cellular phosphorus compounds into the ambient medium with
concomitant breakdown of cellular nucleic acids and accelerated potassium efflux. These events
began rapidly and extensively after addition of the drug.
Clotrimazole is very poorly absorbed following dermal application.
Gentamicin-Betamethasone-Clotrimazole: By virtue of its three active ingredients,
Vetromax ointment has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal activity.
In component efficacy studies, the compatibility and additive effect of each of the components
were demonstrated. In clinical field trials, gentamicin sulfate, betamethasone valerate, and
clotrimazole ointment was effective in the treatment of otitis externa associated with bacteria and
Malassezia pachydermatis. Gentamicin sulfate, betamethasone valerate, and clotrimazole
ointment reduced discomfort, redness, swelling, exudate, and odor, and exerted a strong
antimicrobial effect.
INDICATIONS:
Vetromax ointment is indicated for the treatment of canine acute and chronic otitis externa associated with yeast (Malassezia pachydermatis, formerly Pityrosporum canis) and/or bacteria susceptible to gentamicin.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
If hypersensitivity to any of the components occurs, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Concomitant use of drugs known to induce ototoxicity should be avoided. Do not use in dogs with known perforation of eardrums.
WARNINGS:
The use of gentamicin sulfate, betamethasone valerate, and clotrimazole ointment
has been associated with deafness or partial hearing loss in a small number of sensitive dogs
(e.g. geriatric). The hearing deficit is usually temporary. If hearing or vestibular dysfunction is
noted during the course of treatment, discontinue use of Vetromax ointment immediately and
flush the ear canal thoroughly with a nonototoxic solution.
Corticosteroids administered to dogs, rabbits, and rodents during pregnancy have resulted in
cleft palate in offspring. Other congenital anomalies including deformed forelegs, phocomelia,
and anasarca have been reported in offspring of dogs which received corticosteroids during
pregnancy.
Clinical and experimental data have demonstrated that corticosteroids administered orally or
parenterally to animals may induce the first stage of parturition if used during the last trimester of
pregnancy and may precipitate premature parturition followed by dystocia, fetal death, retained
placenta, and metritis.
PRECAUTIONS:
Identification of infecting organisms should be made either by microscopic roll
smear evaluation or by culture as appropriate. Antibiotic susceptibility of the pathogenic
organism(s) should be determined prior to use of this preparation.
If overgrowth of nonsusceptible bacteria, fungi, or yeasts occur, or if hypersensitivity develops,
treatment should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
Administration of recommended doses of Vetromax ointment beyond 7 days may result in
delayed wound healing.
Avoid ingestion. Adverse systemic reactions have been observed following the oral ingestion of
some topical corticosteroid preparations. Patients should be closely observed for the usual signs
of adrenocorticoid overdosage which include sodium retention, potassium loss, fluid retention,
weight gain, polydipsia, and/or polyuria. Prolonged use or overdosage may produce adverse
immunosuppressive effects.
Use of corticosteroids, depending on dose, duration, and specific steroid, may result in
endogenous steroid production inhibition following drug withdrawal. In patients presently
receiving or recently withdrawn from corticosteroid treatments, therapy with a rapidly-acting
corticosteroid should be considered in especially stressful situations. Before instilling any
medication into the ear, examine the external ear canal thoroughly to be certain the tympanic
membrane is not ruptured in order to avoid the possibility of transmitting infection to the middle
ear as well as damaging the cochlea or vestibular apparatus from prolonged contact.
TOXICOLOGY:
Clinical and safety studies with gentamicin sulfate, betamethasone valerate, and clotrimazole ointment have shown a wide safety margin at the recommended dose level in dogs (see PRECAUTIONS/SIDE EFFECTS).
SIDE EFFECTS:
Gentamicin: While aminoglycosides are absorbed poorly from skin, intoxication may occur when aminoglycosides are applied topically for prolonged periods of time to large wounds, burns, or any denuded skin, particularly if there is renal insufficiency. All aminoglycosides have the potential to produce reversible and irreversible vestibular, cochlear, and renal toxicity.
Betamethasone: Side effects such as SAP and SGPT enzyme elevations, weight loss,
anorexia, polydipsia, and polyuria have occurred following the use of parenteral or systemic
synthetic corticosteroids in dogs. Vomiting and diarrhea (occasionally bloody) have been
observed in dogs and cats.
Cushing's syndrome in dogs has been reported in association with prolonged or repeated
steroid therapy.
Clotrimazole: The following have been reported occasionally in humans in connection with the use of clotrimazole: erythema, stinging, blistering, peeling, edema, pruritus, urticaria, and general irritation of the skin not present before therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The external ear should be thoroughly cleaned and dried before treatment. Remove foreign material, debris, crusted exudates, etc., with suitable non-irritating solutions. Excessive hair should be clipped from the treatment area. After verifying that the eardrum is intact, instill 4 drops from the 7.5 g and 15 g tube of Vetromax twice daily into the ear canal of dogs weighing less than 30 lbs. Instill 8 drops from the 7.5 g and 15 g tube twice daily into the ear canal of dogs weighing 30 lbs. or more. Massage external ear canal carefully after instillation to ensure appropriate distribution of medication. Therapy should continue for 7 consecutive days.
HOW SUPPLIED:
Vetromax ointment is available in:
7.5 g NDC 17033-282-75 tubes
15 g NDC 17033-282-15 tubes
215 g NDC 17033-282-24 tubes
STORAGE:
Store between 2° and 25°C (36° and 77°F).
Shake well before use when using the 215g bottle.
TO OPEN:
Use cap to puncture seal.
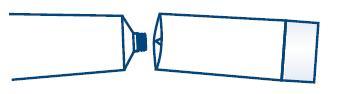
1. Remove entire Applicator Assembly, puncture tube with white portion of the cap.
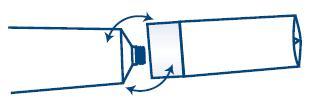
2. Replace entire Applicator Assembly.
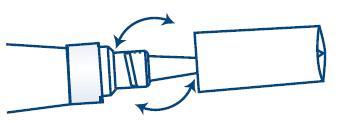
3. To dispense, remove the white portion of the cap.
4. After use replace white cap to close.
IMPORTANT:
The opening of this product is covered by a metal tamper-resistant seal.
If this seal has been punctured or is not visible, do not use and return product to place of purchase.